Architecture
The architecture of pdns-distribute provides the following properties:
- event-based
- message-driven
- scalable
- self-healing
- secure by simplicity
- automation
It is intended to be fast, stable, secure and automatable.
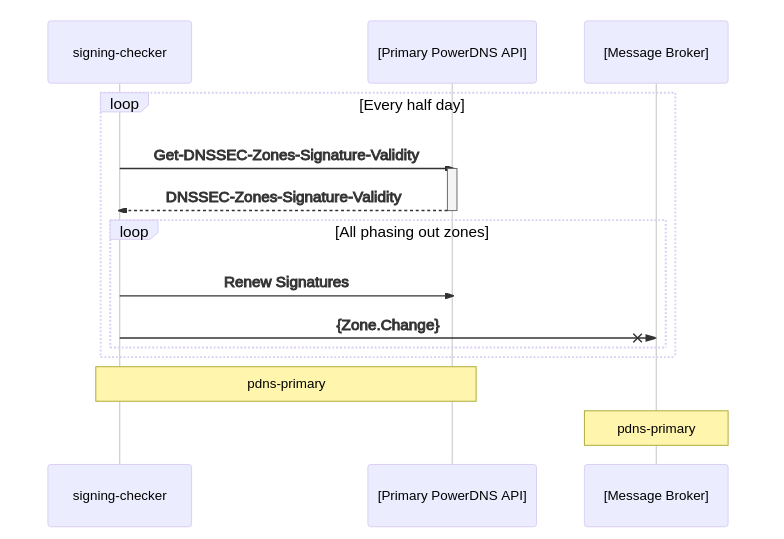
Overview
The architecture consists of four parts (primary, secondary, message broker / nats). It is recommended to have one primary and multiple secondary servers. Multiple Primaries can be used if the database is replicated. In case of multiple primaries it is important to run the health-checker service on only one instance, due to race conditions by running multiple health-checkers within the same cluster.Nontheless there must be at least one secondary. It is recommended to also run the message broker (nats) on at least three instances with jetstream enabled. Those instances can run on separate servers or on primaries and secondaries.
Components
Nats / message broker
The message broker provides the communication backend for every microservice. Nats were chosen because it is very lightweight and powerful. The broker is also used to detect active secondaries.
Security
Nats clusters have to use encryption (TLS) between each instance. Encryption (TLS) and authentication are required for all connections to nats.
Local connections (e.g. to powerdns) are not encrypted, without instances of nats.
The api-proxy enforces encryption. If no TLS keys are provided, it will create self-signed keys automatically at startup. The authentication with the powerdns api uses a token within the http(s) header. The api-proxy will copy the given headers for requests to the powerdns api.
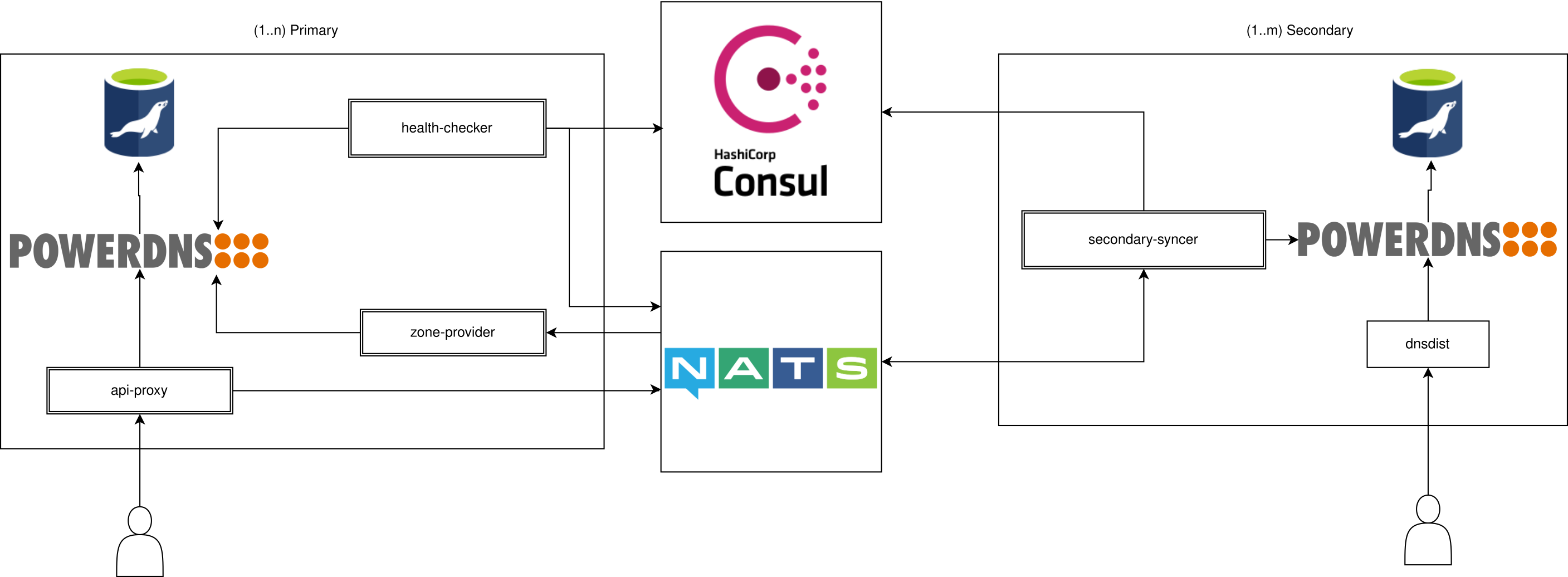
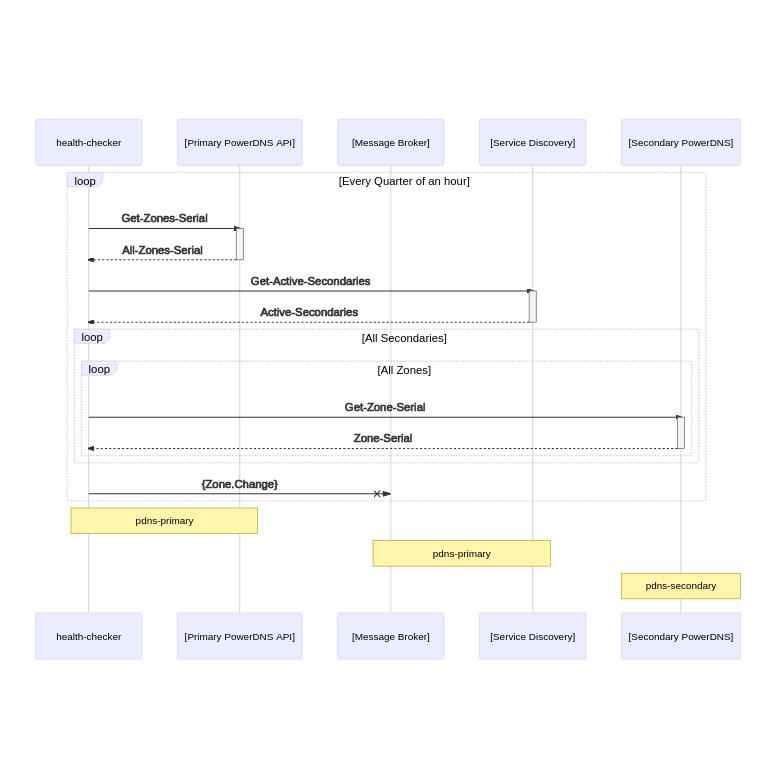
Sequence diagrams
Event Sync
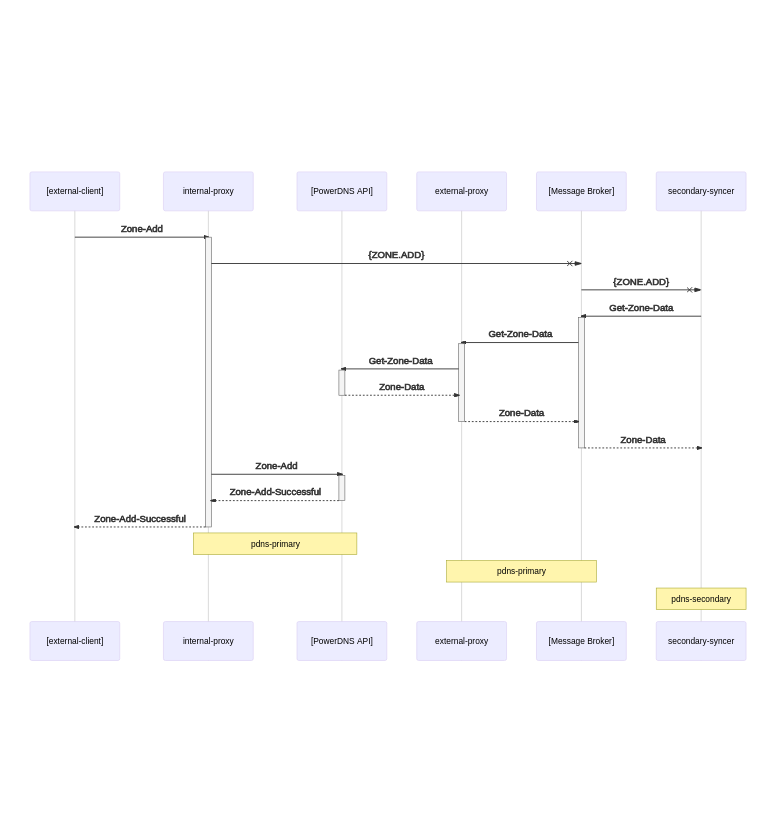
Health Check and trigger Sync
Event based health check
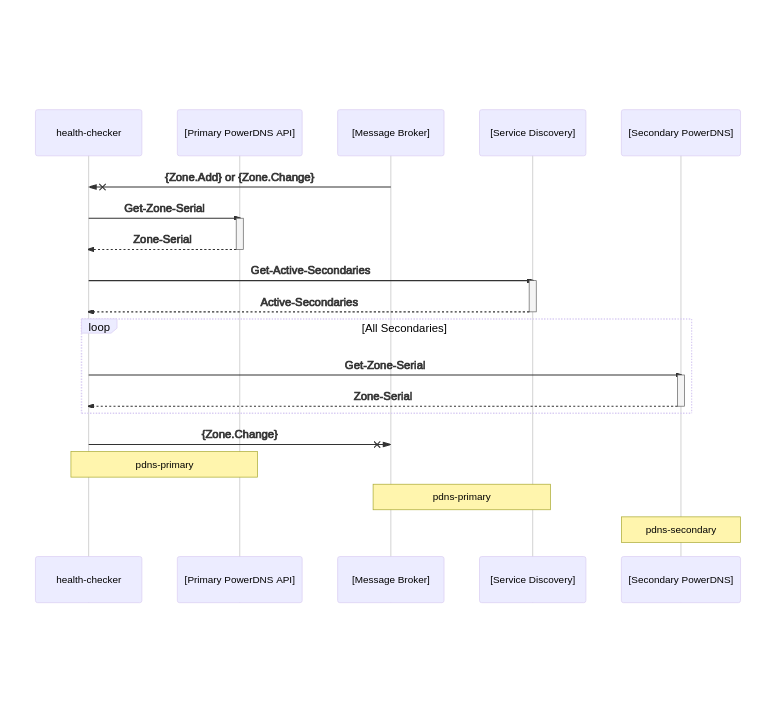
RRSIG Signing Check and Sync